Understand how the Gravimetric Method works
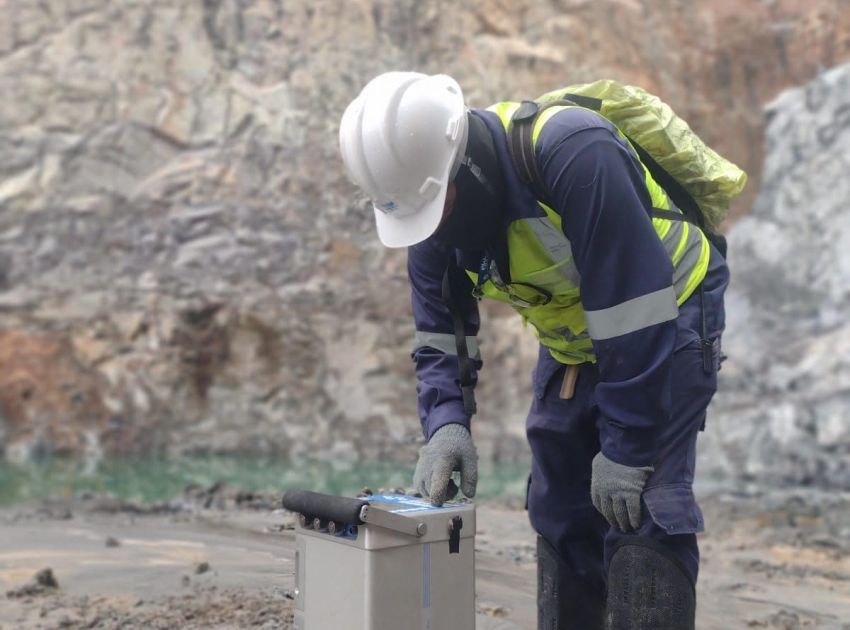
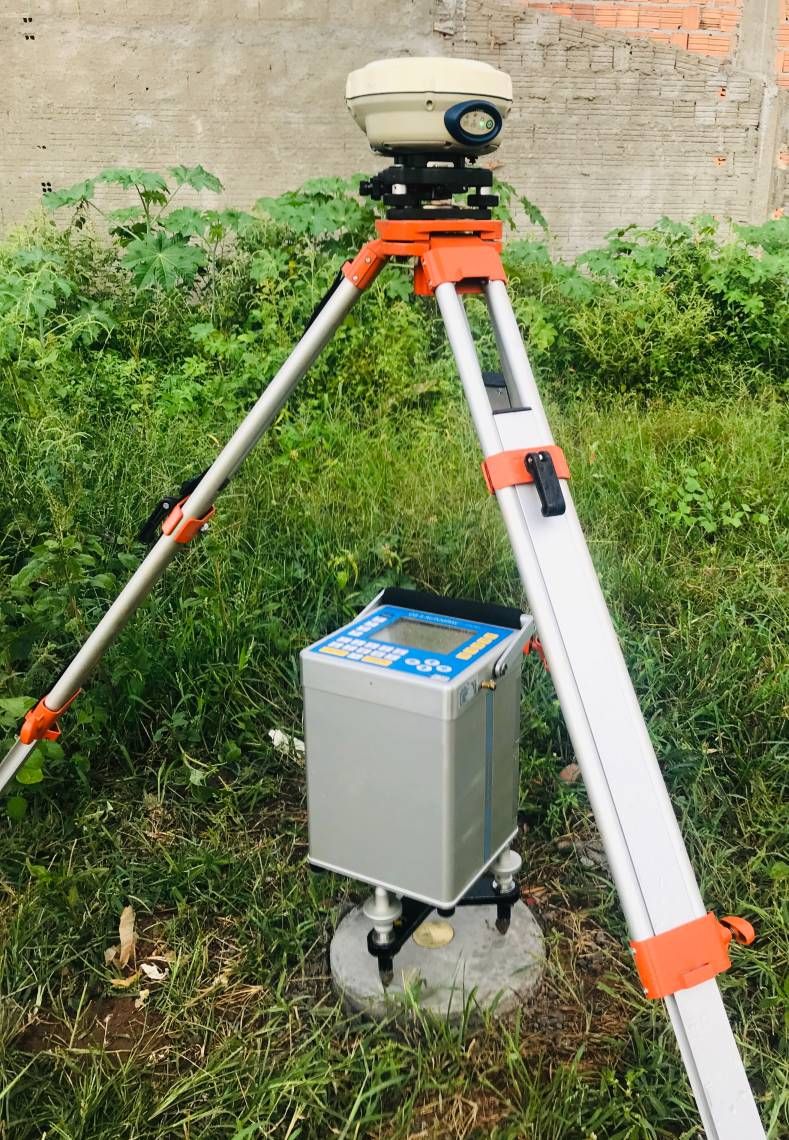
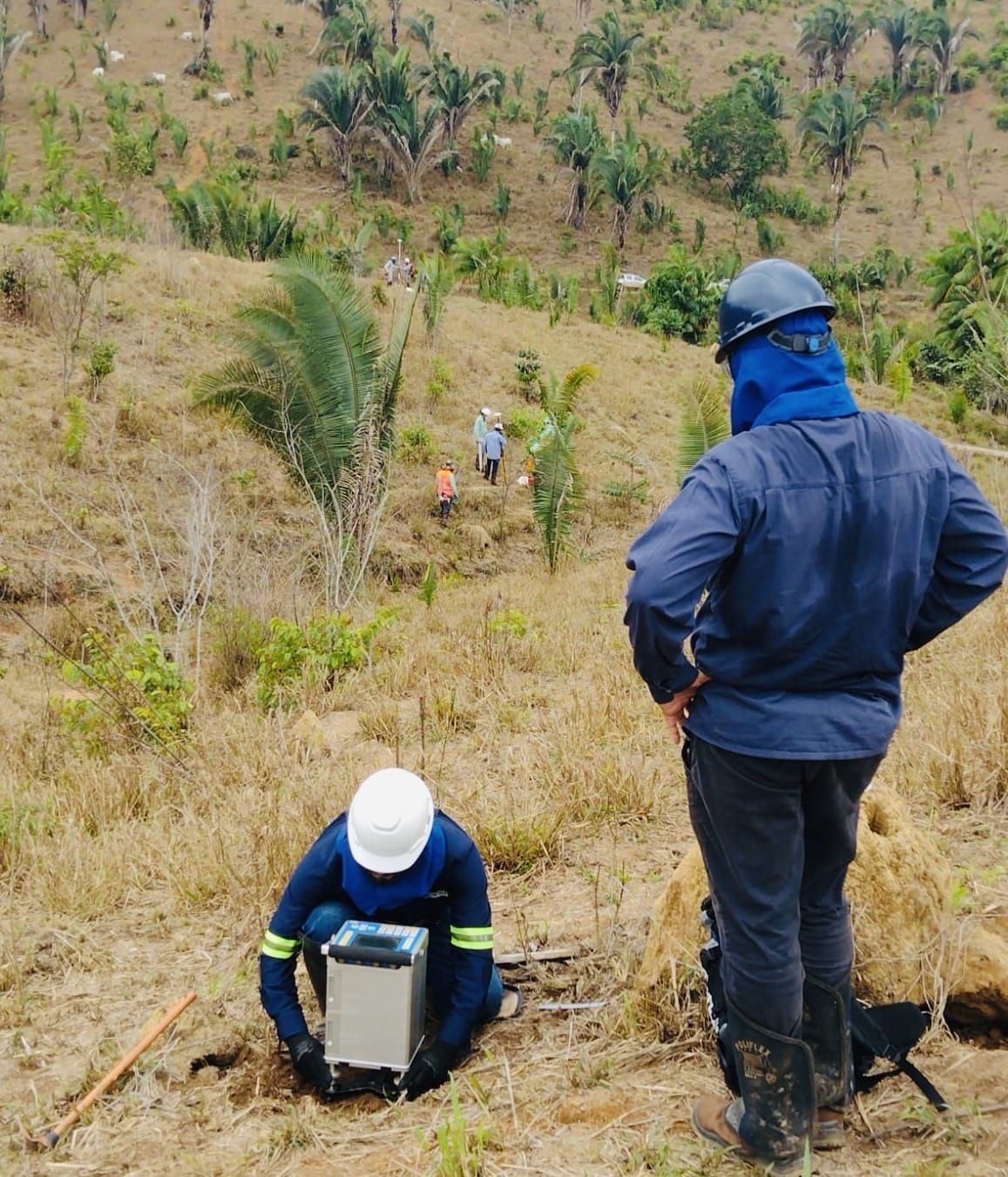
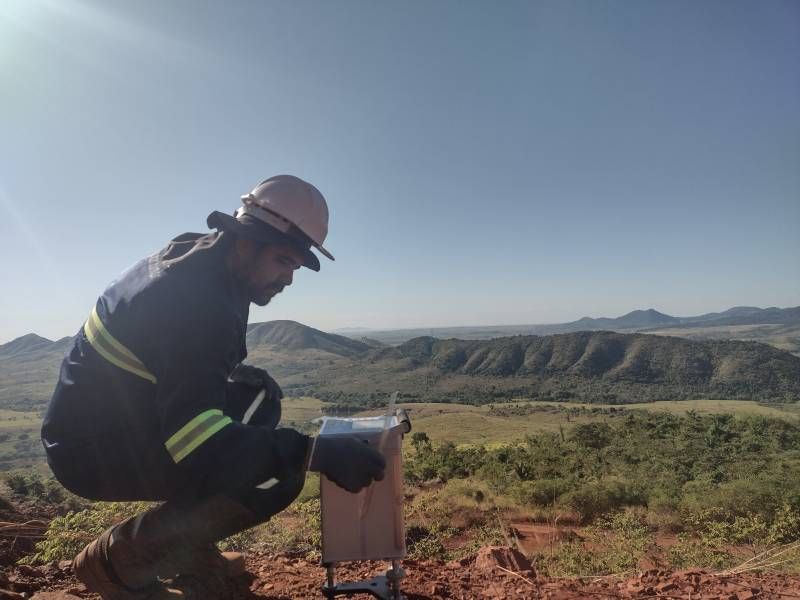
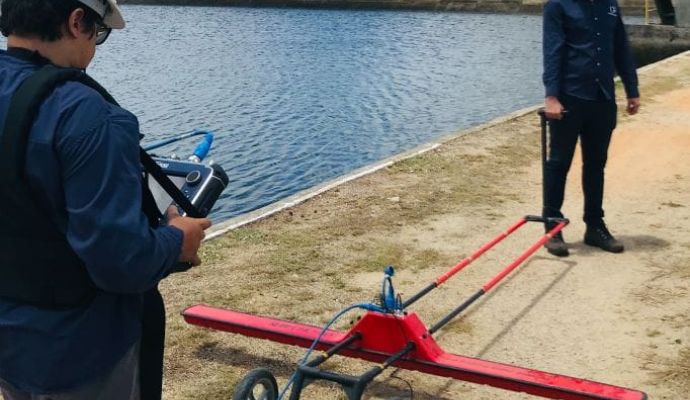
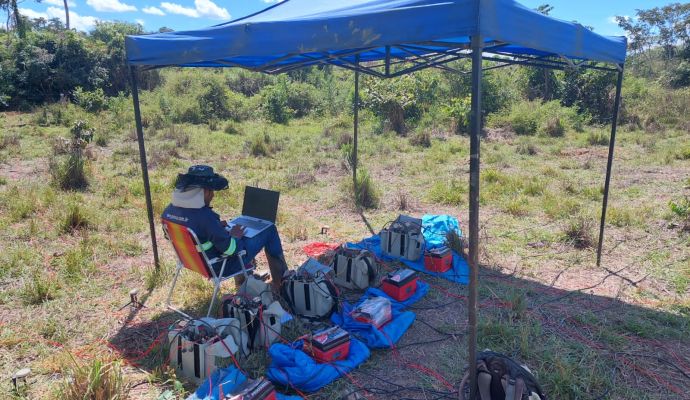
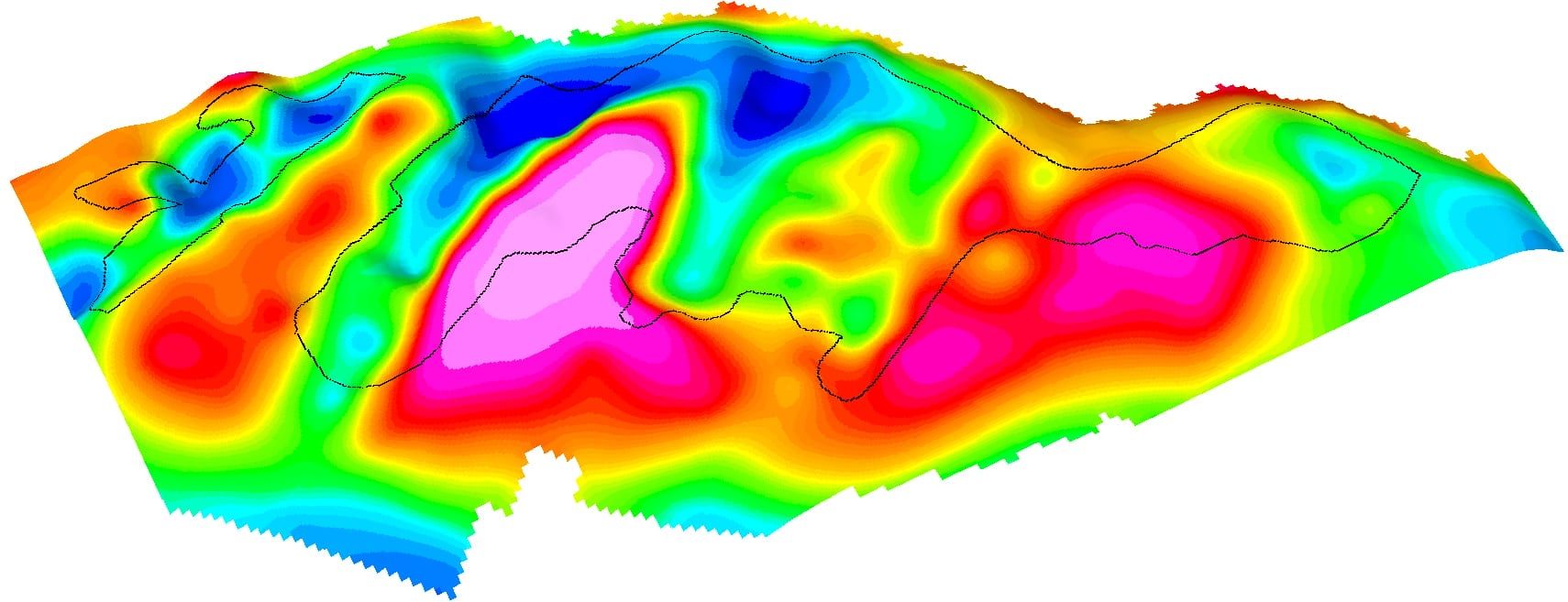
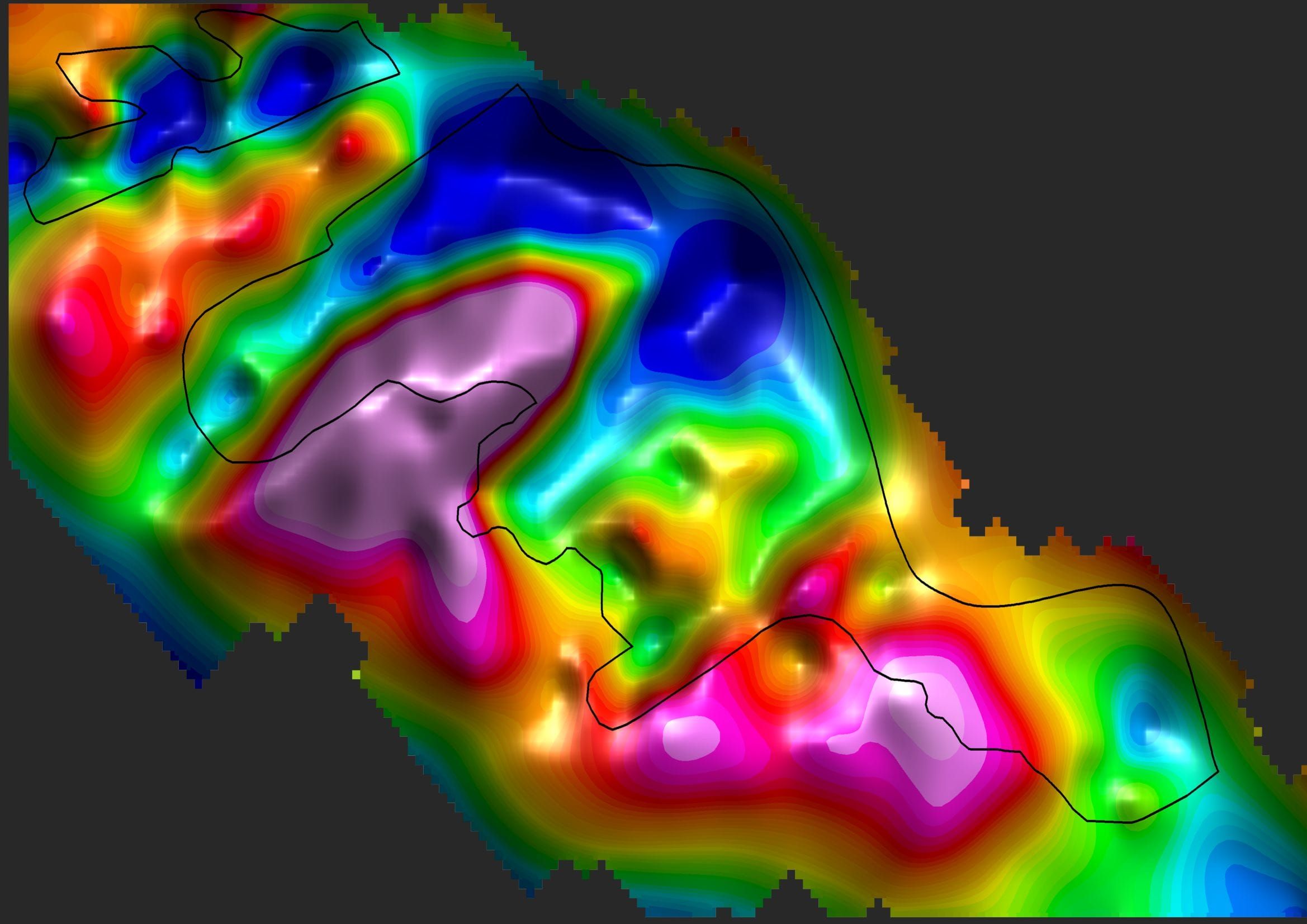
Gravimetry is a geophysical method that consists of measuring the acceleration of gravity at predetermined points on the surface of the terrain. This process aims to map density contrasts of materials in the subsurface, allowing the detection of local variations in the Earth’s gravitational field due to lateral changes in the Earth’s density.
These variations, known as gravimetric anomalies, result from differences in density between various rocks in the Earth’s subsurface. The application of gravimetry in prospecting encompasses the search for oil and gas storage structures, as well as economically relevant mineral deposits, such as chromite, iron and copper sulfides, for example. This method offers valuable insights into the distribution of mass in the subsurface, revealing the presence of rocks with different densities.